Understanding what medical records insurance companies can access is crucial for protecting your privacy and ensuring fair coverage. This guide breaks down the types of medical records insurers can legally review, how HIPAA regulates access, and how you can control the flow of your sensitive health information.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Insurance companies can access only medical records relevant to claims or policies.
HIPAA regulations restrict unauthorized access to your protected health information (PHI).
Patients have the right to limit access and monitor who sees their records.
Using a secure system like My Medical Records enhances your control and privacy.
Knowing your rights helps prevent data misuse and protects your insurance eligibility.
Table of Contents

In today’s data-driven world, your medical records are some of your most sensitive and valuable personal information. From pre-existing conditions to prescription history, the details in your health documents can significantly affect how insurance companies handle your claims or coverage. Whether you’re applying for a new policy or filing a claim, it’s important to understand exactly what insurance companies are legally allowed to access—and what they are not.
Health insurance providers and other third-party payers often require access to certain parts of your medical history to determine eligibility, assess risk, or approve procedures. However, strict federal laws like HIPAA exist to prevent insurance companies from overstepping their boundaries. In this article, we’ll explore which parts of your medical record are fair game, how privacy laws work, and what you can do to keep your health information safe.
Understanding HIPAA and Insurance Access
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was enacted to protect patients’ private health information. It regulates how covered entities, including insurance companies, can handle your Protected Health Information (PHI). PHI includes your full medical history, diagnoses, test results, and any other identifying health data.
Insurance companies can only access your PHI with your written consent or if it’s required for treatment, payment, or healthcare operations. Even then, they are only permitted to review information directly related to the claim or policy in question. For example, if you’re filing a claim for a knee surgery, the insurance provider shouldn’t be accessing unrelated mental health records or unrelated past conditions.
It’s also worth noting that under HIPAA, you have the right to request an accounting of disclosures. This means you can see exactly who accessed your medical records and when, giving you better control over your data and helping you stay alert for any suspicious activity.

What Types of Records Can Insurers Request?
When you submit an insurance application or claim, you typically sign a release form authorizing the insurer to collect relevant medical records. The scope of the request usually depends on the purpose:
Health Insurance Claims: For ongoing treatment or claims processing, insurance companies may request diagnosis reports, lab tests, prescriptions, surgical notes, and physician summaries.
Life or Disability Insurance Applications: These require a more comprehensive history, including past surgeries, chronic illnesses, and possibly mental health evaluations.
Auto or Workers’ Comp Claims: Only medical information tied directly to the incident or injury in question should be reviewed.
It’s essential to read any medical record release forms carefully. While you want your claim to be processed efficiently, it doesn’t mean you have to open your entire history. Many people choose to use a secure online platform to control access, ensuring they share only the necessary files for specific insurance purposes.
If you’re wondering how long medical records need to be kept, the answer varies by state and provider—but it’s typically several years. This means insurers could access older records if permitted, which is another reason to manage your documentation actively.

Can You Limit What Insurers See?
Yes, to a degree. You can choose to restrict what records are shared by being specific in your authorization form. If you’re uncomfortable granting full access, request that your healthcare provider only release documentation pertinent to your condition or claim.
Additionally, consider where you store your medical records. A centralized, secure platform like My Medical Records allows you to manage your files and grant access only when absolutely necessary. Rather than having every doctor’s office send scattered documents to insurers, you can be the gatekeeper of your data.
This is especially important when it comes to sensitive information like mental health treatment, substance use history, or genetic testing. While some insurance providers might ask for broad permissions, you have every right to say no or narrow the scope of access.

Sharing Medical Records Safely and Efficiently
One of the key challenges patients face is not knowing how to easily share medical records without compromising privacy. Faxing documents or giving blanket permissions can lead to oversharing. That’s why secure, cloud-based tools are changing the game.
Using a service like My Medical Records gives you peace of mind and allows you to upload, organize, and share files securely. With built-in encryption and user-level access control, you remain in charge of who sees what—and for how long.
Whether you’re switching insurance plans or disputing a claim, efficient sharing of your records can speed up the process while maintaining data security. Most insurance providers also prefer receiving files digitally, as it simplifies their internal workflows and prevents document loss.

When Do Insurers Request Medical Records?
Medical records are not always requested at the outset of a policy or claim. In many cases, they are requested later for clarification or verification purposes. Typical scenarios include:
Pre-authorization of procedures or medications that require validation of need.
Suspicion of fraud or incomplete disclosures on an application.
Appeals or disputes where additional documentation is needed to support your case.
Be cautious of any unusual or overly broad request. It’s always a good idea to ask the insurer why they need specific documents and consult your provider before signing any release forms.
If you’re still unsure about what your medical record number is and how to find it, it’s typically listed on documents from your healthcare provider, insurance card, or through your digital records portal. Knowing this number can make managing and referencing your medical records significantly easier.
Know Your Rights and Stay Proactive
Navigating the healthcare and insurance system can be complex, but being proactive about your medical records makes a big difference. It’s not just about compliance—it’s about protecting your personal health information from being mishandled or used unfairly.
You also have the right to correct inaccuracies in your records, especially if they affect insurance decisions. If an insurer has denied a claim or delayed processing due to incorrect or incomplete records, you can take steps to fix that by working with your provider or legal representative.
If you need help organizing your documentation, or just want to know more about the technology behind this platform, feel free to learn more about My Medical Records or contact our team directly for support.
Helpful Tips for Managing Insurance Access to Medical Records
Be clear and specific when granting access to insurers. Use secure platforms like My Medical Records to limit and track what files are being shared. Always review what you’re consenting to, and never feel obligated to share your full history if it's not relevant.
Summary:
The relationship between insurance companies and medical records is governed by federal privacy laws, but it’s still up to you to stay vigilant. Insurance companies should only have access to relevant medical information, and not your entire health history. Platforms like My Medical Records, the AI solution for insurance and legal medical documentation, empower you to protect, store, and manage your sensitive health data with ease.
Related Topics:
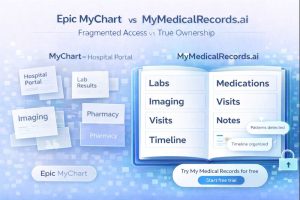
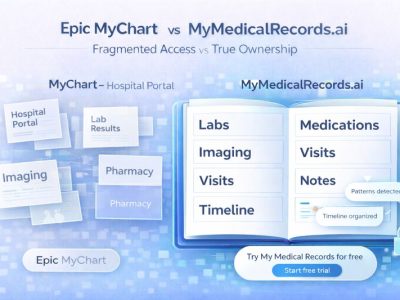
Epic MyChart vs. MyMedicalRecords.ai: Portal Access vs. True Ownership
Epic MyChart vs. MyMedicalRecords.ai: Portal Access vs. True Ownership Meta description: Epic MyChart only shows records from one hospital system. MyMedicalRecords.ai aggregates 100% of your
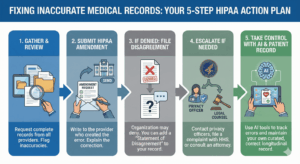
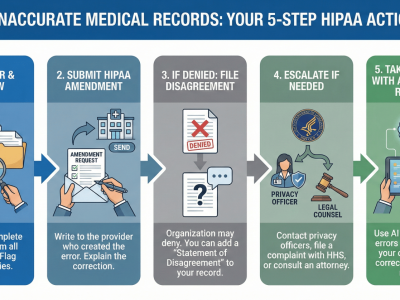
What to Do If There Is Inaccurate Data in Your Medical Record
The chart that does not match you You probably discovered the inaccurate medical records error because something routine went wrong: a prior authorization denied, a

From Chaos to Clarity: A Family Caregiver’s Guide to Unified Health Records
Here’s what nobody tells you about caregiving: The hardest part isn’t watching your loved one struggle with their diagnosis. It’s trying to keep track of
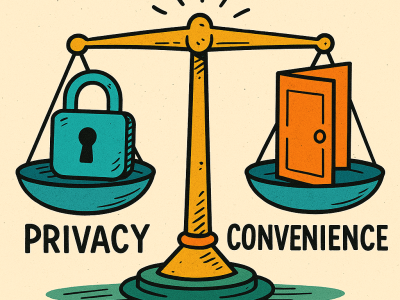
Privacy vs Access: Finding the Right Balance in Your Digital Health Record
Healthcare interoperability is the ability of different healthcare systems, devices, and applications to seamlessly share, understand, and use patient data across organizations and geographic boundaries.

Healthcare Interoperability: Why Systems Can’t Connect
Healthcare interoperability is the ability of different healthcare systems, devices, and applications to seamlessly share, understand, and use patient data across organizations and geographic boundaries.

How to Merge Medical Records from Multiple Doctors and Avoid Errors & Duplicates
Learn how to merge medical records from multiple doctors, avoid duplicate entries, and reduce errors. Use AI tools like My Medical Records to simplify the process.